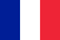
What is chronic prostatitis? First, you need to understand what the prostate is, it is also the prostate gland. It is an organ found only in the body of males, develops during fetal development and persists throughout life. The prostate is an external secretory gland, i. e. he reveals his secret and brings it out.
Due to its location, it is not visible from the outside because. in the pool in men. It is a rounded formation that is located below the bladder, yet in the immediate vicinity of the pelvic floor, rectum, ureters, urethra, and vascular and nerve braids of the pelvis. Since this organ is an externally secreted gland, it is necessary to understand what functions it performs. First, it produces a secret that is an important component of male sperm. This secret involves a lot of protein, amino acids, and so on.
Unfortunately, both men and doctors pay little attention to the prostate.
So what is prostatitis chronic prostatitis in particular
This is an inflammatory disease of the prostate. This inflammation can be acute or chronic.
No chronic disease starts spontaneously, it is always preceded by some degree of acute inflammation.
In some cases, the man may not notice the onset of the disease, but it persists for a long time and cannot be cured and then leads to severe morphological and functional abnormalities.
Chronic prostatitis usually develops at least three months after the acute inflammation of the prostate.
As a result of inflammation, the morphology of the cell composition is upset and the functions of the prostate are impaired.Epidemiology

This disease is one of the most common inflammatory diseases among men. The disease is quite young, meaning men of different ages are exposed. If prostate adenoma is more common in old age, chronic prostatitis can occur in men and at age 20 years of age. The average age at which symptoms of the disease are observed is 40-50 years.
By old age, almost all men suffered from the disease, but many of them could not even treat it and did not seek medical attention for certain symptoms.
However, in chronic prostatitis, the symptoms may not appear immediately and the man may turn to other problems that he thinks are more serious. And it is only before the treatment of another disease that the initial cause becomes clear. If treated improperly in acute inflammation, chronic prostatitis is unavoidable.
Causes of chronic prostatitis
In particular, predisposing factors should be identified when identifying the cause of prostatitis. There are a lot of them and they are very common in the modern world.
These are primarily infectious agents. The cause is more often a microbial etiology. The microbial infection may be nonspecific or may carry a specific pathogen. Specific agents include sexually transmitted infections. And given that many of these infections in men can be completely asymptomatic, so they can persist in the body for a long time. Even the most contemplated chronic infection can lead to prostatitis.
The appearance of non-specific pathogens can be caused by non-compliance with personal hygiene rules and infrequent washing of the penis acorns both after urination and shortly after intercourse.
In some cases, vaginal dysbiosis in a partner or some opportunistic pathogens in women play a huge role in the development of male prostatitis.
The most common pathogens of inflammation include chlamydia, trichomonads, gonococci, gardnerella, E. coli, staphylococci, and enterococci.
Don’t forget the likelihood of viruses and fungi being involved
In this case, the pathogen enters the body on an ascending route, i. through the urethra.
In addition, there is another important way the infectious agent penetrates - hematogenous. Many men have some form of inflammatory disease, and sometimes the flu or SARS can cause an inflammatory process.
Hypothermia, decreased immunity, and even overheating in the background of an infection already present in the body can also provoke the development of inflammation.
Sexual behavior also plays an important role in the development of an inflammatory reaction. In this case, prolonged sexual abstinence negatively affects the condition of the gland, contributing to stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs, disruption of blood supply, and slowing of blood circulation in the organ.
Interrupted sexual intercourse, incomplete depletion of sperm cells lead to entrapment of secretions in the organ, and a crowded, enlarged organ can affect blood supply processes and even cause slight swelling of the surrounding tissues. In rare cases, the disease is immunological. An autoimmune factor is not excluded either. Chronic somatic infection should also be ruled out.
Symptoms and treatment of chronic prostatitis
Many men do not have symptoms of chronic prostatitis at all. Some people may not even be able to pinpoint one or the other predisposing factor. However, this disease has many symptoms. The most popular of these is pain. The pain syndrome can be quite long, sometimes lasting months.
Pain is often not localized to a specific location. It is usually diffuse in nature and tends to irradiate the lower back, perineum, scrotum, groin regions. But they are by no means point-like. They most often pull and hurt, the pains are not lasting. They increase or decrease depending on the condition of the body and the influence of environmental factors.
Another important sign is the violation of the sexual sphere. Men can often complain of erectile dysfunction, which is almost imperceptible at first and occurs much later in its later stages, even if they are exposed to all predisposing factors.
But there is never complete impotence in chronic prostatitis. So is ejaculation. At first, it may appear much faster than planned, and later, on the contrary, it will slow down to almost complete cessation. Orgasm becomes less vivid and more emotionally expressed. Sometimes problems with the sexual sphere can affect the partner. A very common cause after which men are diagnosed with chronic prostatitis is infertility.
Men also often have urination problems. It will be fast, sometimes reminiscent of signs of cystitis. A compulsive urge to urinate can disturb a man at night. Sometimes pain, cramps, etc. A man may also experience symptoms of chronic prostatitis on his own.
How to diagnose chronic prostatitis in a timely manner and start immediate and effective treatment?
It is usually not difficult for professionals with such a profile. If a man experiences any symptoms, the doctor may make this diagnosis without further examination.
The minimum examination is usually limited to a medical history, laboratory tests, and digital rectal examination, and digital rectal examination does not require additional preparation in a man. Your doctor can determine the size, consistency, and pain of your prostate in a particular area.
Laboratory indicators are not limited to general blood testing. Urine analysis is also required, in which case it has certain characteristics. The man must deliver the last dose of urine, called the terminal, in which the laboratory technician must determine the number of leukocytes and the presence of bacterial cells. In some cases, the pathogen is not found and must be tested for sexually transmitted infections.
They also take a smear from the urethra. Another very important part of the diagnostic plan is ultrasound. It is performed through the rectum using a special sensor. They determine the size of the gland, scars, tumors, edema, and so on. presence. It is also important to control the blood supply to the organ.
In some more severe and asymptomatic cases, an invasive biopsy may be required.
To rule out cancer, a man can be sent to test for a tumor marker of prostate cancer in the blood. It's called PSA. But you should take it no earlier than 10 days after the digital rectal examination.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
The sooner you start treatment for chronic prostatitis, the more likely it is that the disease will go out of its chronic form. Never resort to self-treatment, as prostatitis should be treated by a qualified professional.
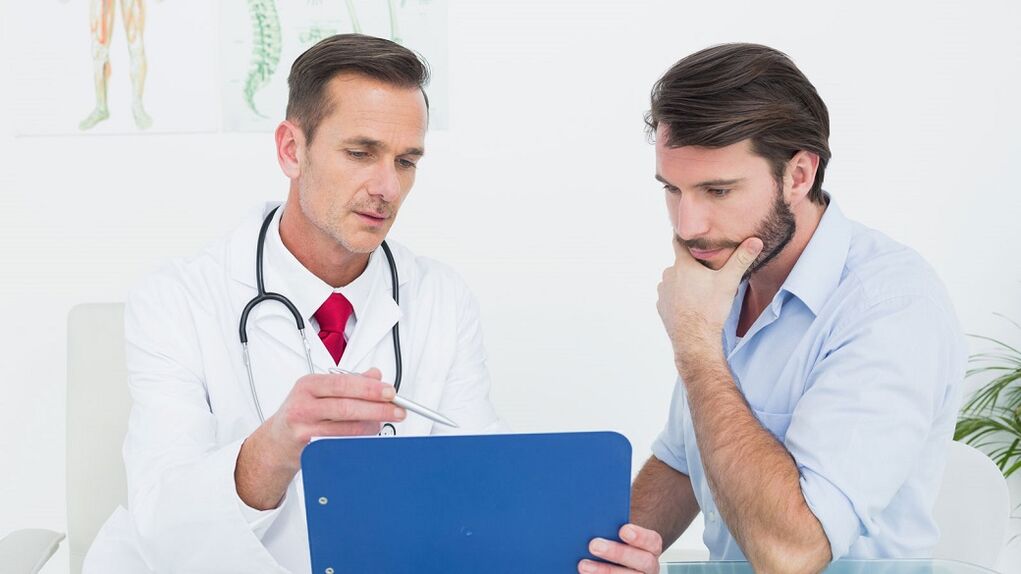

This pathology is treated by a urologist. Generally, treatment does not require hospitalization. All existing chronic diseases need to be treated.
First of all, you need to start with a lifestyle change. Casual sexual intercourse and partner illness should be ruled out.
You must follow personal hygiene rules. Rinse your penis thoroughly to prevent bacteria from accumulating under your foreskin. Sex life should be regular with complete ejaculation. Coitus interruption should be avoided.
In addition, physical activity should be increased. Exercise more often to prevent blood stagnation in the pelvis and prostate.
The diet also needs to be adjusted. Try to avoid fast food, spicy, smoked and salty foods. Sweets should also be restricted. Alcohol and drugs should be completely avoided. Men should also stop smoking.
The treatment of prostatitis is also divided into medical and surgical treatment. First, with chronic prostatitis, they naturally begin to treat the cause. And since it is most contagious, antibiotics are the main drug. Its selection depends primarily on the pathogen detected during diagnosis. It is best to immediately determine the susceptibility of the microorganism to antibacterial agents.
This will make treatment more effective and shorter. Antibiotics can be prescribed by several routes of administration. In the case of an asymptomatic process, tablet forms are usually prescribed. If the chronic process worsens, they will resort to injectable medications. The treatment of chronic prostatitis can involve several devices at the same time.
An important component of complex treatment is anti-inflammatory drugs. This is usually a class of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Vasodilators are also usually very necessary to improve the blood supply to the pelvic organs and to restore microcirculation. They prevent congestion.
Another group of agents used are immunomodulators. Vitamin therapy should also be included in the complex treatment.
Surgical methods are rarely resorted to, but sometimes this is the only way out. Of these methods, resection of the prostate is used. In some cases, surgical treatment of complications is required. This may be an excision of a cyst or an opening in an abscess.
The treatment of chronic prostatitis also includes various physiotherapies. In order for a disease such as chronic prostatitis to have a favorable prognosis, the identified disease should be treated immediately. The effectiveness of the treatment should be checked by a specialist after a while.